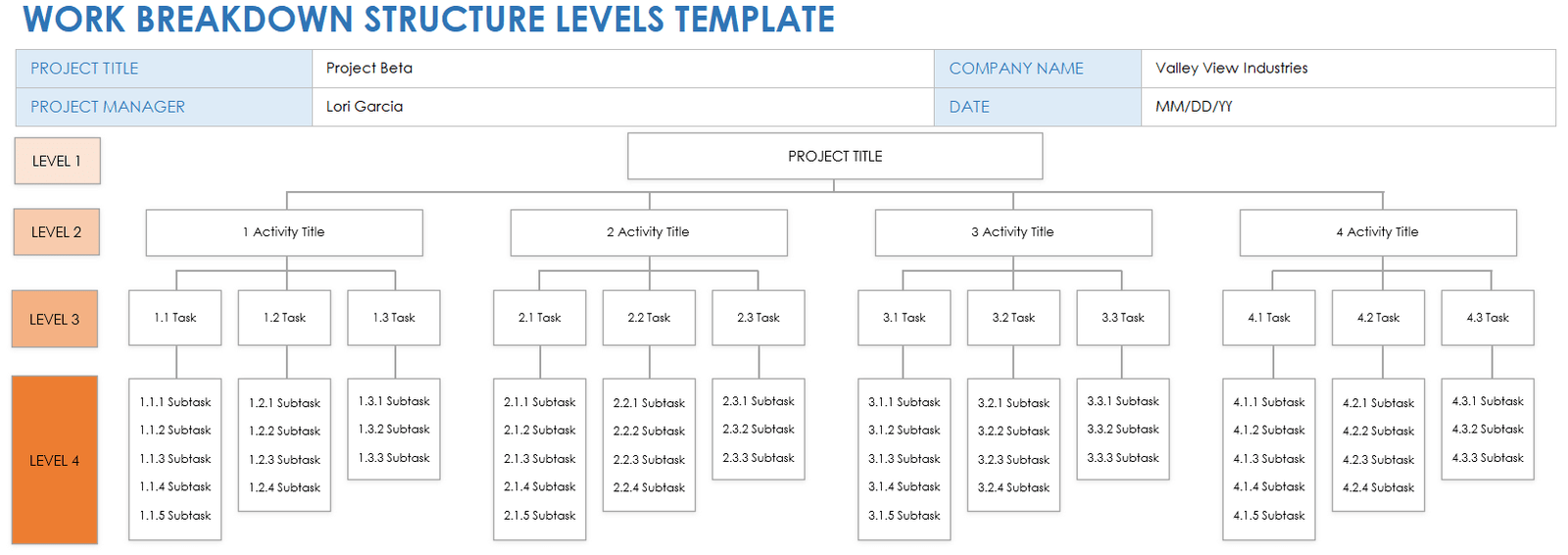
Identifying the Key Benefits:
These templates offer several advantages that contribute to successful project execution:
- Standardization: Templates ensure a consistent approach to project management, reducing variability and promoting uniformity across projects. This standardization simplifies training and onboarding processes for new team members.
- Time Efficiency: By providing pre-designed structures, templates save time in the planning and documentation phases. Project managers can focus more on execution and less on creating documents from scratch.
- Enhanced Communication: Templates improve communication by presenting information in a clear, organized manner. Stakeholders can quickly grasp project status, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Risk Management: Using templates helps identify potential risks early in the project lifecycle. Templates often include sections for risk assessment and mitigation strategies, ensuring proactive risk management.
- Improved Tracking: These templates facilitate tracking progress against established benchmarks. This tracking enables project managers to identify deviations and take corrective actions promptly.
Related Article: Construction Project Management
Types of Project Management Templates:
Here are the 10 common types explained below:
- Project Charter: A project charter template outlines the project’s purpose, objectives, scope, and stakeholders. It serves as a foundational document that authorizes the project’s initiation.
- Project Plan: A project plan template details the project’s tasks, timelines, resources, and milestones. It provides a roadmap for project execution and ensures alignment with project goals.
- Gantt Chart: A Gantt chart template visualizes the project schedule, showing task durations, dependencies, and critical paths. It aids in tracking progress and identifying potential bottlenecks.
- Risk Management Plan: A risk management plan template identifies potential risks, assesses their impact, and outlines mitigation strategies. It ensures proactive risk management throughout the project lifecycle.
- Budget Plan: A budget plan template details the project’s financial aspects, including estimated costs, actual expenditures, and variances. It helps in monitoring financial performance and ensuring budget adherence.
- Communication Plan: A communication plan template outlines how project information will be disseminated to stakeholders. It includes communication channels, frequency, and responsibilities.
- Status Report: A status report template provides a snapshot of the project’s progress, highlighting achievements, issues, and upcoming tasks. It keeps stakeholders informed and facilitates decision-making.
- Change Request: A change request template documents proposed changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget. It includes a detailed description, impact assessment, and approval process.
- Lessons Learned: A lessons learned template captures insights and experiences from completed projects. It helps in improving future projects by documenting successes and areas for improvement.
- Project Closure: A project closure template formalizes the project’s completion, documenting final deliverables, lessons learned, and stakeholder sign-off. It ensures a structured project closure process.
Download: Project Management Documentation Templates
Identifying the 10 Key Components:
These effective templates share several key components that contribute to their utility:
Header Information: The header includes basic project details such as project name, manager, start date, and end date. It provides a quick reference for identifying the document’s purpose and scope.
Objectives: Clearly defined objectives outline what the project aims to achieve. These objectives guide project activities and provide a basis for measuring success.
Scope: The scope section details the project’s boundaries, including what is included and excluded. It helps prevent scope creep and ensures that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the project’s extent.
Related Article: Project Dashboard Template
Stakeholders: Identifying stakeholders and their roles is crucial for effective communication and collaboration. This section lists key stakeholders, their interests, and their responsibilities.
Timeline: A timeline provides a visual representation of the project schedule, highlighting key milestones and deadlines. It helps in tracking progress and ensuring timely completion of tasks.
Budget: The budget section outlines the project’s financial plan, including estimated costs, actual expenditures, and variances. It enables monitoring of financial performance and ensures budget adherence.
Risk Assessment: A comprehensive risk assessment identifies potential risks, evaluates their impact, and outlines mitigation strategies. It ensures proactive risk management and reduces the likelihood of project derailment.
Resource Allocation: Resource allocation details the resources required for the project, including personnel, equipment, and materials. It ensures that resources are available when needed and helps in avoiding resource conflicts.
Communication Plan: The communication plan outlines how project information will be shared with stakeholders. It includes communication channels, frequency, and responsibilities, ensuring that stakeholders remain informed and engaged.
Performance Metrics: Performance metrics provide a basis for measuring project success. These metrics may include key performance indicators (KPIs) such as completion rates, budget adherence, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Related Article: Work Breakdown Structure Template
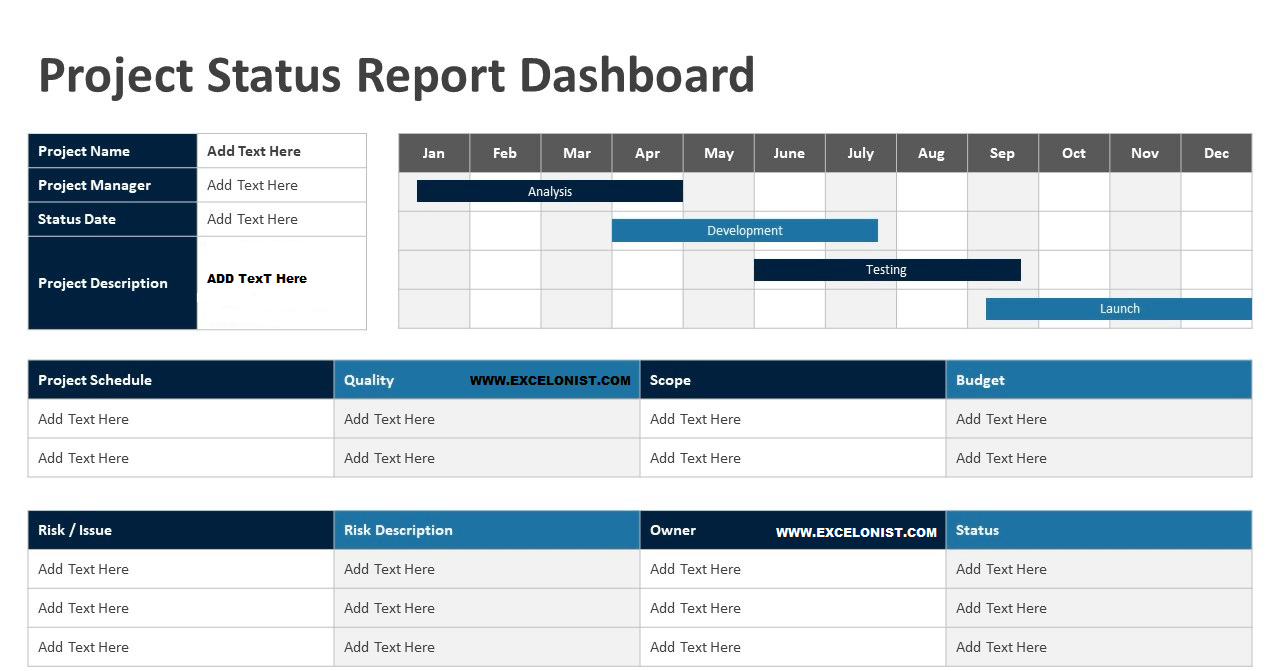
Creating Effective Project Management Templates:
Creating these templates involves several steps discussed below:
- Identify Needs: Determine the specific needs of your project or organization. This includes understanding the types of projects you manage, the stakeholders involved, and the information required for successful project execution.
- Research Best Practices: Research industry best practices and standards for project management. This helps in ensuring that your templates align with established methodologies and provide relevant information.
- Customize Templates: Customize templates to fit your organization’s unique requirements. This may involve adding specific sections, adjusting terminology, or incorporating branding elements.
- Test and Refine: Test the templates in real projects to identify any gaps or areas for improvement. Gather feedback from project managers and stakeholders, and refine the templates accordingly.
- Train Users: Provide training for project managers and team members on how to use the templates effectively. This ensures that everyone understands the purpose of each template and how to complete them accurately.
- Review and Update: Regularly review and update the templates to ensure they remain relevant and effective. This involves incorporating lessons learned from completed projects and staying informed about changes in project management practices.
Also Checkout: Inventory Tracking Template Excel
What are Some Common Challenges?
While these templates offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges:
- Over-Reliance on Templates: Relying too heavily on templates can lead to a lack of flexibility and creativity. Project managers should use templates as guides rather than rigid frameworks, allowing room for adaptation based on project-specific needs.
- Inadequate Customization: Templates that are not adequately customized may fail to address unique project requirements. It is important to tailor templates to fit the specific context and needs of each project.
- Resistance to Change: Introducing new templates can face resistance from team members who are accustomed to existing processes. Effective change management, including training and communication, is essential for successful template adoption.
- Template Maintenance: Regularly updating and maintaining templates can be time-consuming. Organizations must allocate resources for template review and updates to ensure their continued relevance and effectiveness.
Related Article: Project Management Office – Wikipedia
Conclusion:
These Templates serve as invaluable tools for ensuring consistency, efficiency, and success in project execution. By providing standardized structures for planning, execution, and monitoring, these templates streamline processes and enhance communication among stakeholders. In 2024, the integration of advanced technology further amplifies the benefits of Project Management Templates, enabling real-time collaboration, data-driven decision-making, and increased productivity. To maximize their effectiveness, organizations must customize templates to fit their unique needs, provide adequate training, and regularly review and update templates based on lessons learned and evolving best practices.


