A project plan is a comprehensive document that serves as a roadmap for a project. It outlines the project’s objectives, scope, timeline, resources, tasks, and potential risks. The project plan provides a structured approach to manage and execute the project efficiently, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page and working towards a common goal.
Here’s a breakdown of what a project plan typically includes:
- Project Objectives: Clearly defined goals and objectives that the project aims to achieve.
- Project Scope: The boundaries of the project, detailing what is included and what is not included.
- Project Deliverables: Specific outcomes or products that the project will produce.
- Project Timeline: A schedule that outlines the sequence of activities, milestones, and deadlines.
- Resource Allocation: Identification of the human resources, equipment, and materials needed for the project.
- Budget: An estimate of the project’s overall cost, including labor, materials, and any other expenses.
- Risk Management: Identification of potential risks that could affect the project, along with strategies to mitigate them.
- Communication Plan: A plan for how communication will be handled within the project team and with stakeholders.
- Quality Management: Standards and processes for ensuring the quality of project deliverables.
- Change Management: Procedures for managing changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget.
- Closure: Plans for wrapping up the project, including project review, documentation, and handover of deliverables.
Related Article: 10+ Tips For Designing Action Plan Template – PMITOOLS
Overall, a project plan provides a structured approach to manage all aspects of a project from initiation to closure. It serves as a guide for the project manager and team members to ensure that the project is completed successfully, on time, and within budget.

Who is responsible for planning projects?
Several stakeholders are involved in planning projects, but the primary responsibility typically falls on the project manager. Here’s a breakdown of who is responsible for planning projects:
Project Manager:
-
- The project manager is ultimately responsible for all aspects of the project, including planning.
- They oversee the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure.
- The project manager creates the project plan, ensuring that it aligns with the project’s objectives, scope, and constraints.
- They coordinate with stakeholders, team members, and resources to develop and execute the project plan.
- Throughout the project, the project manager monitors progress, manages changes, and ensures that the project stays on track.
Project Team:
-
- While the project manager leads the planning process, the project team members contribute their expertise and insights.
- Team members provide input on tasks, timelines, resource requirements, and risks within their areas of responsibility.
- They collaborate with the project manager to develop detailed plans for their assigned tasks or work packages.
Stakeholders:
-
- Stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, and other relevant parties, provide input into the project plan.
- They communicate their requirements, expectations, and constraints to the project manager.
- Stakeholders review and approve the project plan to ensure it meets their needs and aligns with organizational goals.
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs):
-
- SMEs contribute specialized knowledge and insights related to specific aspects of the project.
- They may assist in developing plans for technical tasks, quality assurance, risk management, or other areas where their expertise is required.
Functional Managers:
-
- Functional managers oversee departments or teams within the organization.
- They may provide input on resource allocation, availability of personnel, and adherence to organizational standards and policies.
Project Management Office (PMO):
-
- In organizations with a PMO, this department may provide support and guidance for project planning processes.
- The PMO may establish templates, standards, and best practices for project planning and ensure that project managers adhere to them.
- In some cases, organizations may hire external consultants or contractors to assist with project planning, especially for specialized projects. External Consultants or Contractors: These individuals or firms contribute their expertise to develop aspects of the project plan, such as risk analysis, financial planning, or technical design.
Related Article: 9 Useful Tips To Create A Rolling Action Item List – PMITOOLS
Importance of Project Plan:
A project plan is vital for the successful execution of any project. It serves as a roadmap, guiding the team through the project’s objectives, scope, timeline, and resources. By clearly defining goals, tasks, and deliverables, a project plan ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Project Plan Template:
A Project Plan Template is a pre-designed framework that outlines the key components of a project plan. It provides a structured format for documenting project objectives, scope, timelines, resources, risks, and other essential details.
For Project Management Templates Visit: Project Management Documents Templates (ucube.biz)
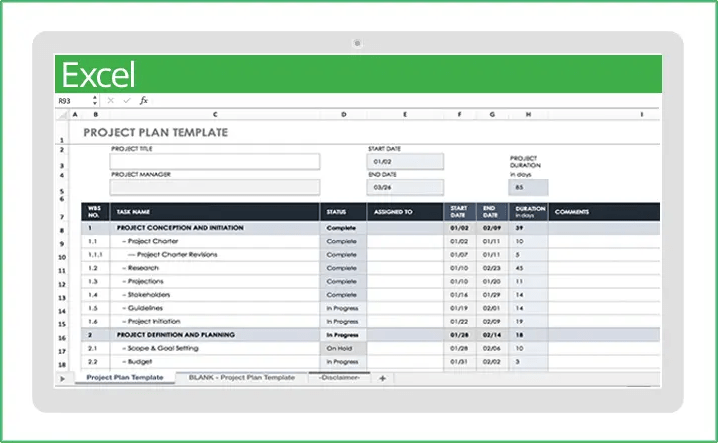
Tips to create a Project Plan Template:
Creating a good project plan template is essential for setting up a project for success. Here are some tips to help you create an effective and efficient project plan template:
Keep It Simple:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or technical terms.
- Keep the layout clean and uncluttered.
Start with Key Sections:
- Begin with essential sections like Project Overview, Objectives, Scope, Timeline, Resources, and Risks.
- Add additional sections as needed for specific project requirements.
Define Clear Objectives:
- Clearly state the project’s objectives and goals.
- Make sure objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Include Detailed Scope:
- Define the project’s boundaries and deliverables.
- Clearly state what is included and what is excluded from the project.
Break Down Tasks:
- Break the project into smaller tasks or work packages.
- Provide space for task descriptions, responsible parties, and deadlines.
Use a Timeline:
- Include a timeline or Gantt chart to visualize the project schedule.
- Highlight important milestones and deadlines.
Allocate Resources:
- List all required resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials.
- Specify resource availability and allocation.
Budgeting:
- Include a budget section with estimates for all project costs.
- Break down costs into categories such as labor, materials, equipment, and overhead.
Address Risks:
- Identify potential risks and include a risk management section.
- Outline strategies for mitigating or managing each risk.
Communication Plan:
- Specify how communication will be handled within the project team and with stakeholders.
- Define communication channels, frequency, and key contacts.
Quality Assurance:
- Outline quality standards and procedures for ensuring deliverables meet requirements.
- Include quality control checkpoints throughout the project lifecycle.
Change Management:
- Develop a process for managing changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget.
- Define how changes will be evaluated, approved, and implemented.
Templates and Examples:
- Provide templates and examples for various sections to guide users.
- Include instructions and tips for completing each section.
Customization:
- Make the template adaptable to different project types and sizes.
- Include optional sections or modules that can be added or removed as needed.
Review and Revision:
- Review the template regularly to ensure it remains relevant and up-to-date.
- Incorporate feedback from users and update the template accordingly.
Accessibility:
- Ensure the template is accessible to all project stakeholders.
- Use a format that is compatible with common software tools and platforms.
Training and Support:
- Provide training and support for using the template effectively.
- Offer assistance and guidance as needed to users.
Encourage Documentation:
- Encourage users to document project decisions, actions, and outcomes using the template.
- Emphasize the importance of keeping the project plan updated throughout the project lifecycle.’
Related Article: Project plan – Wikipedia
Conclusion:
Overall, a well-developed project plan is essential for staying organized, on track, and ultimately, for achieving project success.



